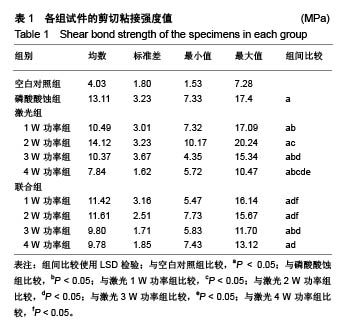
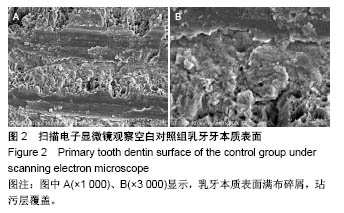
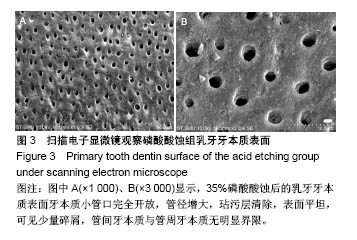
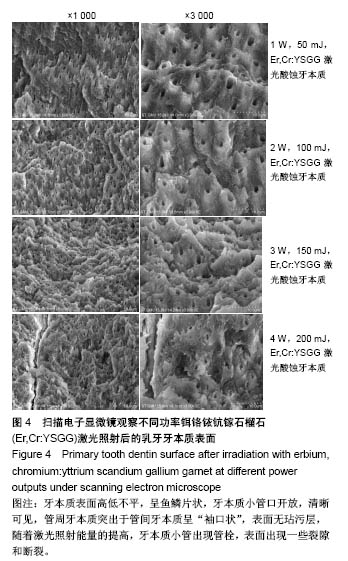
| [1] Soares CJ,Fonseca RB,Martins LR,et al.Esthetic rehabilitation of anterior teeth affected by enamel hypoplasia: a case report.J Esthet Restor Dent.2002;14(6):340-348.[2] Buonocore MG.A simple method of increasing the adhesion of acrylic filling materials to enamel surfaces.J Dent Res. 1955; 34(6):849-853.[3] Pires PT,Ferreira JC,Oliveira SA,et al.Shear bond strength and SEM morphology evaluation of different dental adhesives to enamel prepared with ER:YAG laser.Contemp Clin Dent. 2013; 4(1):20-26.[4] Beer F,Buchmair A,Korpert W,et al.Morphology of resin-dentin interfaces after Er,Cr:YSGG laser and acid etching preparation and application of different bonding systems. Lasers Med Sci. 2012;27(4):835-841.[5] Hossain M,Nakamura Y,Yamada Y,et al.Effects of Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation in human enamel and dentin: ablation and morphological studies.J Clin Laser Med Surg. 1999;17(4): 155-159.[6] Santini A,Plasschaert AJ,Mitchell S.Effect of composite resin placement techniques on the microleakage of two self-etching dentin-bonding agents.Am J Dent.2001;14(3):132-136.[7] Yap AU,Pearson GJ,Billington RW,et al.An in vitro microleakage study of three restorative techniques for Class II restorations in posterior teeth.Biomaterials. 1996;17(21): 2031-2035.[8] Wigdore H,Abt E,Ashrafi S,et al.The effect of lasers on dental hard tissues.J Am Dent Assoc. 1993;124(2):65-70.[9] Margolis F.The Star Wars of dentistry.Using the erbium laser to treat tooth decay.CDS Rev. 2002;19:26-29.[10] Rizoiu I,Kohanghadosh F,Kimmel AI,et al.Pulpal thermal responses to an erbium,chromium ysgg pulsed laser hydrokinetic system.Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1998;86(2):220-223.[11] Eversole LR,Rizoiu I,Kimmel AI.Pulpal response to cavity preparation by an erbium, chromium:YSGG laser-powered hydrokinetic system.J Am Dent Assoc. 1997;128(8):1099-1106.[12] Hossain M,Nakamura Y,Yamada Y,et al.Compositional and structural changes of human dentin following caries removal by Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation in primary teeth.J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2002;26(4):377-382.[13] Lin S,Pan D,Lin Q,et al.Evaluation of phase, microstructure and composition of human dentine after Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation.J Nanosci Nanotechnol.2011;11(3):2421-2426.[14] Hossain M,Kimura Y,Nakamura Y,et al.A study on acquired acid resistance of enamel and dentin irradiated by Er,Cr:YSGG laser.J Clin Laser Med Surg.2001;19(3):159-163.[15] Al-Omari WM,Palamara JE.The effect of Nd:YAG and Er,Cr:YSGG lasers on the microhardness of human dentin. Lasers Med Sci.2013;28(1):151-156.[16] Vergauwen TE,Michiels R,Torbeyns D,et al.Investigation of Coronal Leakage of Root Fillings after Smear Layer Removal with EDTA or Er,Cr:YSGG Laser through Capillary Flow Porometry. Int J Dent.2014;2014:593160.[17] Wolfram H,Volker R,Elke A,et al.Principles and phenomena of bioengineering with glass-ceramics for dental restoration.J Eur Ceram Soc.2007;27(2-3):1521-1526.[18] Bouillaguet S,Ciucchi B,Jacoby T,et al.Bonding characteristics to dentin walls of class II cavities, in vitro.Dent Mater. 2001; 17(4):316-321.[19] Luthy H,Marinell CP,Scharer P.Factors influencing metal-resin tensile bond strength to filled composites.Dent Mater.1990;6(2): 73-77.[20] Masoumeh M,Leila E,Fekrazad R,et al.The effect of Er,CrYSGG laser and air abrasion on shear bond strength of a fissure sealant to enamel.J Am Dent Assoc. 2010;141(2):157-161.[21] Bona D.Shear vs tensile bond strength of resin composite bonded to creamic.Dent Res. 1999;74:1591-1596.[22] Wang X, Zhang C, Matumoto K. In vivo study of the healing processes that occur in the jaws of rabbits following perforation by an Er,Cr:YSGG laser.Laser Med Sci. 2005;20(1):21-27.[23] Yamada MK,Uo M,Ohkawa S,et al.Three-dimensional topographic scanning electron microscope and Raman spectroscopic analyses of the irradiation effect on teeth by Nd:YAG, Er: YAG, and CO(2) lasers.J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2004;71(1):7-15.[24] Cardoso MV,De Munck J,Coutinho E,et al.Influence of Er,Cr:YSGG laser treatment on microtensile bond strength of adhesives to enamel.Oper Dent.2008;33(4):448-455.[25] Ramos TM,Ramos-Oliveira TM,Moretto SG,et al.Microtensile bond strength analysis of adhesive systems to Er:YAG and Er,Cr:YSGG laser-treated dentin.Lasers Med Sci. 2014;29(2): 565-573.[26] Ayar MK,Yildirim T,Yesilyurt C.Effects of Er,Cr:YSGG laser parameters on dentin bond strength and interface morphology.Microsc Res Tech.2015;78(12):1104-1111.[27] Sungurtekin E,Oztas N.The effect of erbium, chromium: yttrium-scandium-gallium-garnet laser etching on marginal integrity of a resin-based fissure sealant in primary teeth. Lasers Med Sci. 2010;25(6):841-847.[28] Cvikl B,Moser G,Wernisch J,et al.The impact of Er,Cr:YSGG laser on the shear strength of the bond between dentin and ceramic is dependent on the adhesive material.Lasers Med Sci. 2012;27(4):717-722.[29] Issar R,Mazumdar D,Ranjan S,et al.Comparative Evaluation of the Etching Pattern of Er,Cr:YSGG & Acid Etching on Extracted Human Teeth-An ESEM Analysis.J Clin Diagn Res. 2016;10(5): ZC01-05.[30] Malkoc MA,Tasdemir ST,Ozturk AN,et al.Effects of laser and acid etching and air abrasion on mineral content of dentin. Lasers Med Sci.2011;26(1):21-27.[31] Yildirim T,Ayar MK,Yesilyurt C.Influence of different Er,Cr:YSGG laser parameters on long-term dentin bond strength of self-etch adhesive.Lasers Med Sci. 2015;30(9): 2363-2368.[32] Verma M,Kumari P,Gupta R,et al.Comparative evaluation of surface topography of tooth prepared using erbium, chromium: Yttrium, scandium, gallium, garnet laser and bur and its clinical implications.J Indian Prosthodont Soc. 2015;15(1):23-28.[33] Lee BS,Lin PY,Chen MH,et al.Tensile bond strength of Er,Cr:YSGG laser-irradiated human dentin and analysis of dentin-resin interface.Dent Mater.2007;23(5):570-578.[34] Garbui BU,de Azevedo CS,Zezell DM,et al.Er,Cr:YSGG laser dentine conditioning improves adhesion of a glass ionomer cement.Photomed Laser Surg.2013;31(9):453-460.[35] Kinoshita J,Kimura Y,Matsumoto K.Comparative study of carious dentin removal by Er,Cr:YSGG laser and Carisolv.J Clin Laser Med Surg.2003;21(5):307-315.[36] Shahabi S,Zendedel S.Atomic analysis and hardness measurement of the cavity prepared by laser.Lasers Med Sci. 2010;25(3):379-383.[37] Oznurhan F,Olmez A.Morphological analysis of the resin-dentin interface in cavities prepared with Er,Cr:YSGG laser or bur in primary teeth.Photomed Laser Surg. 2013;31(8):386-391.[38] Hossain M,Nakamura Y,Yamada Y,et al.Microleakage of composite resin restoration in cavities prepared by Er,Cr:YSGG laser irradiation and etched bur cavities in primary teeth.J Clin Pediatr Dent.2002;26(3):263-268.[39] Shafiei F,Memarpour M,Fekrazad R.Sealing of silorane-based composite in laser-prepared primary teetheffect of acid etching. Pediatr Dent.2014;36(5):378-383.[40] Malekafzali B,Fekrazad R,Mirfasihi A,et al.Comparison of microtensile bond strength of a resin composite to enamel conditioned by acid etching and Er,Cr:YSGG laser in human primary teeth.Eur Arch Paediatr Dent.2015;16(1):57-62.[41] De Menezes Oliveira MA,Torres CP,Gomes-Silva JM,et al.Microstructure and mineral composition of dental enamel of permanent and deciduous teeth.Microsc Res Tech. 2010;73(5): 572-577.[42] Kamburoglu K,Yetimoglu NO,Altan H.Characterization of primary and permanent teeth using terahertz spectroscopy. Dentomaxillofac Radiol.2014;43(6):20130404.[43] 梁韵,陈柯.Er,Cr:YSGG激光对乳牙硬组织粘接性能影响的研究进展[J].口腔疾病防治, 2017,25(3):196-199. |
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)